The Meaning of an Identity Map
An identity map is a part of Linear Algebra. It is also referred to as identity function, identity relation, identity operator, and identity transformation. So, don't be surprised if we use these terms interchangeably as we proceed.
In Math, a map shows the relationship between two sets of elements. So, you can say that an identity map shows the relationship between elements of different sets.
An identity map is a function that takes an input value and spits out the exact same value for the output.
For example, the function
is an identity function.
Identify maps can also be represented in another way: The function below is also an identity map!
 In an identity map, the domain and co-domain are identical - StudySmarter Originals
In an identity map, the domain and co-domain are identical - StudySmarter Originals
In this image, the elements of the domain are exactly the same as the elements in the co-domain.
In an identity map, a co-domain is a mirror image of the input (domain) values.
The identity map is sometimes denoted as Id(x) = x.
Properties of Identity Maps
Identity maps have a couple of key properties:
The elements in the domain and co-domain of the map are the same (it returns the value of its input).
The graph of an identity function is a straight line with a slope of 1.
Identity Maps Examples
We can also represent an identity map in the form of a graph. The graph of an identity function is a line that passes through the origin. Let's practice identifying identity maps from various formats.
Plot the graph for the following identity function.
Answer:
Plotting the graph gives:
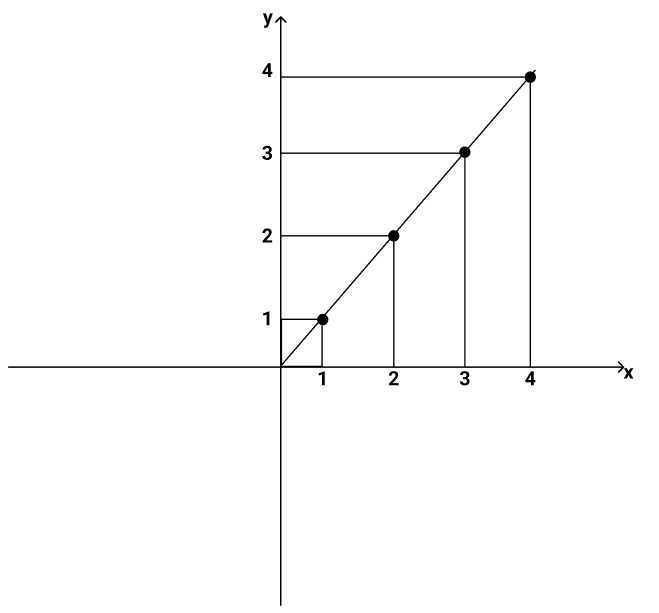
From the graph, you can see that we have a straight line. We take the input as x and the output as y, forming the line. That is, (1, 1), (2, 2), (3, 3), and (4, 4).
Use the table below to plot a graph of the function f(x) and determine if the function is an identity function.
Answer:From the table, we can already tell that the function is an identity function because the values of x and y are the same but let's see what the graph says.
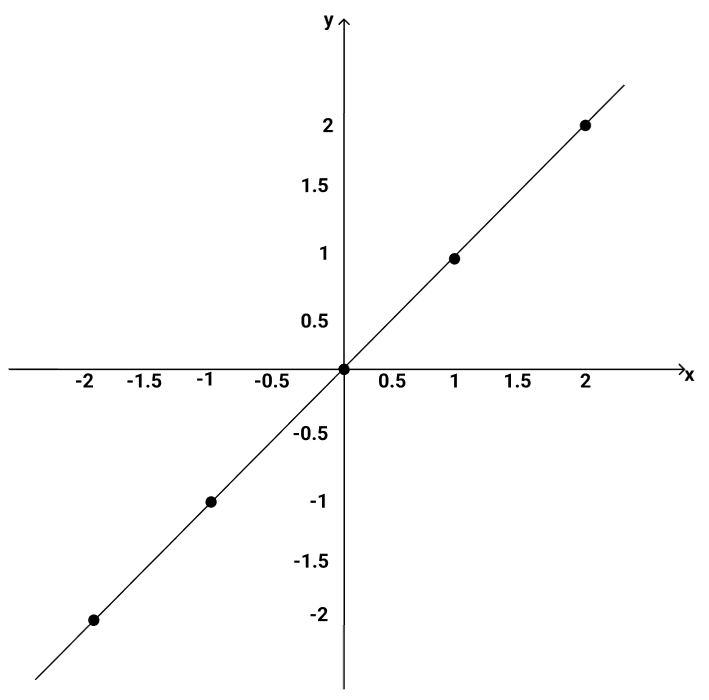
The plot is a line that passes through the origin, indicating that the function is an identity function.
Which of the following image does NOT represent an identity map?
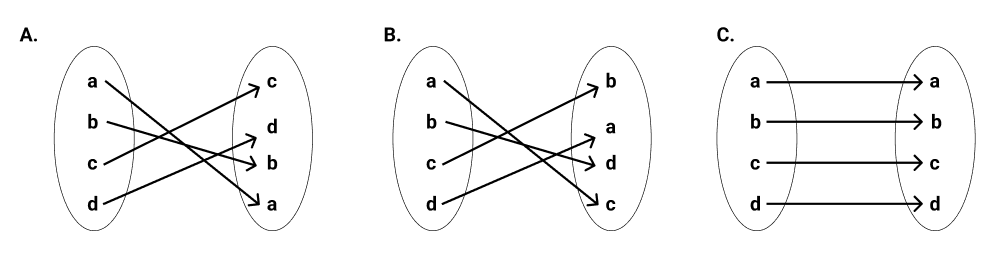
Answer:
This can be a bit tricky, so you have to look closely. If you observe image A, you will see that a maps to a, b maps to b, c maps to c, and d maps to d. The output is an exact image of the input, meaning it is an identity map.
If you observe the second image, a maps to c, b maps to d, c maps to b, and d maps to a. This means that it is not an identity map because the elements do not map to themselves.
From the third image, it's apparent that all elements map to themselves. So, it's an identity map.
So, the answer to the question is B because the elements do not map to themselves.
Prove that is an identity function and draw the identity map.
Answer:
For the function to be identical, the input and output must be identical. So, what we will do here is to plug in different values for x and see if the input and the output will be the same.
If x = 1,
If x = 2,
If x = 4,
If x = 5,
We can see that no matter the value of x, the output and the input will still be equal. This means that the function f is an identical map. The figure below shows the identity map.
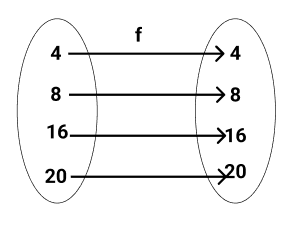
Identity Maps in Linear Algebra
The identity map has a matrix called the identity matrix. An identity matrix is a square matrix where the diagonals have values of 1, and the rest of the matrix is filled with zeros.
Below is an example of a 2 x 2 and a 3 x 3 identity matrix.
A 2 x 2 identity matrix -
A 3 x 3 identity matrix -
The thing with identity matrices is that when you multiply them by themselves, you get the same matrix back. No matter the dimensions of the matrix, you will always get it back when it is multiplied by itself.
Let's see some examples.
What is the result when you square a identity matrix? What about if you square a identity matrix?
Answer:
A identity matrix is:
Squaring the matrix above yields
A identity matrix is
Squaring the matrix above yields
As you can see, when an identity matrix is multiplied by itself, the result is the identity matrix. This is why it is related to an identity map.
You can find details on matrix multiplication in our article Operations with matrices
Identity Maps, Identity Functions, and Identity Transformations
As mentioned, the term "identity maps" is used interchangeably with "identity functions" and "identity transformations" in the Math world.
Identity Map - Key takeaways
- The term "identity map" is used interchangeably with the terms "identity function", "identity relation", "identity operator", and "identity transformation".
- The elements in the domain and co-domain of the map are the same.
- The graph of an identity function is a straight line.
- The identity map has a matrix called the identity matrix.
- The identity matrix consists of ones along the diagonal and zeros everywhere else.












