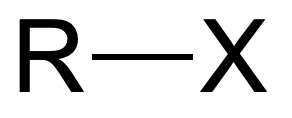Relative Ease of Hydrolysis of Acyl Chlorides, Alkyl Chlorides, and Aryl Chlorides
Hydrolysis is the chemical reaction of a compound with water, in which breakdown of both the compound and water takes place. The ease of hydrolysis differs in different compounds. When we compare alkyl chlorides, acyl chlorides, and aryl chlorides, the order of ease of hydrolysis is - Acyl chloride > alkyl chloride > aryl chloride
Aryl chlorides do not undergo hydrolysis. This can be explained by the strength of carbon-chlorine bond.
Acyl Chlorides
 Fig. 10: Acyl Halide | StudySmarter Originals
Fig. 10: Acyl Halide | StudySmarter Originals
Hydrolysis of acyl halides is easiest compared to alkyl halides and aryl halides, and can be done at
room temperature. This is because the carbon that the halide is attached to, is also attached to an oxygen atom. The oxygen atom and the halide atom are both very electronegative and pull electron away from the carbon atom. As a result, the
carbon atom is left very δ+. This makes the C-X bond weak, making it an easy site for a nucleophile to attack.
Alkyl Halides
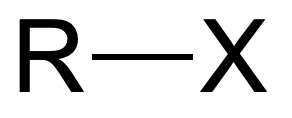
Fig. 11: Alkyl Halide | StudySmarter Originals
In alkyl halides, there is only one electronegative atom, the halogen, pulling electrons away from the carbon atom which it is attached to. Therefore, the carbon atom is not as δ+, and the C-X bond is stronger than that in acyl halides. Therefore, hydrolysis of alkyl halides needs to be heated, and also to be refluxed with OH-, which is a stronger nucleophile than H2O.
Aryl Halides
The C-X bond in aryl halides is the strongest. This is because a lone pair of electrons on the halide atom is part of the delocalized 𝜋-bonding. This results in the C-X bond in developing some double-bond characteristics. Therefore, hydrolysis of aryl halides does not occur.
Let us look at the resonance structures that aryl halides exhibit in the example of aryl chloride.
 Fig. 12: Resonance Structures of Aryl Chloride | Cliffs Notes
Fig. 12: Resonance Structures of Aryl Chloride | Cliffs Notes
As you can see in the resonance structures diagram, 3 out of 4 resonance structures have a double bond between the carbon atom and the chlorine atom. Therefore, in the hybrid structure, there are some double bond characteristics in the C-X bond.