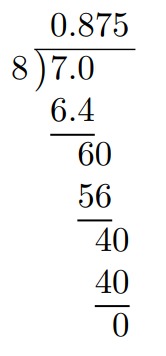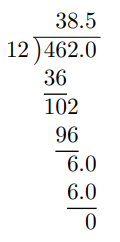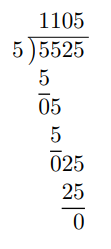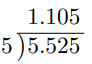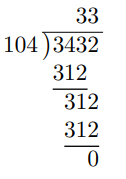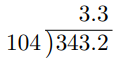
Example 1, Aishah Amri - StudySmarter Originals
At first glance, we could definitely represent this number as a fraction. As we have seen from earlier articles, fractions express numbers that are not whole numbers. In this case, we would have the fraction . What if I told you that there is another way to write numbers that are not whole? That's right! These are called decimals.
In this article, we are going to explore decimals, its definition, operations on decimals, mixed operations and many examples.
Decimals
Let us begin with the definition of a decimal.
A decimal is a number that contains a decimal point.
The decimal point is represented by a dot and separates a whole number from its fractional part. The value of the fractional part is always less than one. The number of digits formed by the fractional part determines the number of decimal places. Let us demonstrate the position of decimals on a number line to give us a clearer picture of this concept. This is displayed below.
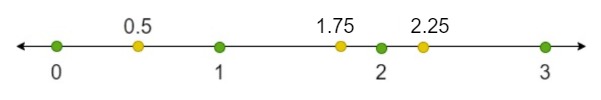
Example 2, Aishah Amri - StudySmarter Originals
Another way to look at decimals is by representing them in a place value table. This will help us identify the number of decimal places for each decimal value given which is important to notice when performing operations involving decimals. Let us construct this place value table below.
| Thousands | Hundreds | Tens | Ones | Decimal Point (.) | Tenths | Hundredths | Thousandths |
| 1000 | 100 | 10 | 1 | . | 0.1 | 0.01 | 0.001 |
The digits before the decimals point represent the whole part of the number while the digits after the decimal point represent the decimal part of the number.
Given the decimal 12.45, the position for each number is defined below.
| Digit | 1 | 2 | . | 4 | 5 |
| Place Value | Tens | Ones | Decimal place | Tenths | Hundredths |
| The number associated with place value | 10 | 2 | . | 0.4 | 0.05 |
In some textbooks, the fractional part is also referred to as the decimal part.
The decimal number 3.4512 has 3 as its whole number component and 0.4512 as its fractional part.
There are four decimal places here since there are four digits after the decimal point.
Recap: Converting Fractions to Decimals
Method 1: Using A Calculator
The easiest way to convert a fraction to a decimal is by using a calculator. Simply divide the numerator by the denominator. Plugging these digits into your calculator will give you your answer.
Method 2: Long Division
Use long division to convert into a decimal.
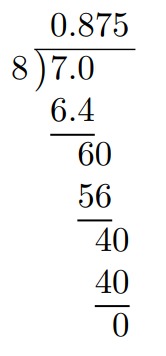
Therefore,
Recap: Converting Percentages to Decimals
Recall that a percentage takes the form . To convert a percentage to a decimal, all we have to do is remove the % sign and divide the remaining digit by 100. This is done by moving the decimal point two spaces to the left.
Convert 45% to a decimal.
Moving two spaces to the left, we obtain 45% = 0.45
Convert 3.67% to a decimal.
Moving two spaces to the left from the decimal point, we obtain 3.67% = 0.0367
Order of Operations
When performing basic arithmetic operations on decimals such as addition, subtraction, multiplication and division, we must take into account the order of operations. This is particularly important when dealing with mixed operations involving decimals. The order of operations for decimals is abbreviated by the acronym PEMDAS, described in the table below.
| Order | Letter | Concept | Explanation |
| 1 | P | Parenthesis | These are expressions inside a pair of parenthesis or brackets such as (x + y) and [x + y] or in the form of a grouping such as |
| 2 | E | Exponent | These are expressions of the form xy |
| 3 | M | Multiplication | These two operations have the same precedence, thus we simply execute the order of operation from left to right |
| 4 | D | Division |
| 5 | A | Addition | These two operations have the same precedence, thus we simply execute the order of operation from left to right |
| 6 | S | Subtraction |
Always remember PEMDAS: Parenthesis, Exponent, Multiplication/Division, Addition/Subtraction.
Adding and Subtracting Decimals
The addition and subtraction of decimals are similar to adding and subtracting integers. We always begin from the right-hand side and apply the column method. The column method helps maintain the place values and decimal places clearly to achieve an accurate summation or deduction between decimals.
Write down the numbers in column form such that their decimal points are lined up vertically;
Put in zeros as place-holders (if necessary) so that the numbers are of the same length;
Add or subtract using column addition or column subtraction;
Place the decimal point back into the sum or difference such that it lines up vertically with the numbers being added or subtracted.
Let us demonstrate this method with some worked examples below.
Do not forget to add the decimal point at the end of your answer!
Add 5.7 and 8.9
Subtract 2.3 from 4.8
Addition and Subtraction of Decimals with Whole Numbers
Remember to add in zeros as place-holders so that the numbers are of the same length! Below are some worked examples that show this.
Add 6 and 4.3
Subtract 5 from 9.2
Addition and Subtraction of Two Unlike Decimals
As before, ensure that the decimals are of the same length by adding in zeros as place-holders. Here are two worked examples that exhibit this.
Add 5.43 and 6.678
Subtract 2.3456 from 4.1
Multiplying Decimals
To multiply decimals, we must consider the rules for multiplying decimals.
Remove the decimal point from the given numbers and carry out multiplication as usual;
Count the number of decimal places in each of the original numbers and find its sum;
The place value of the final answer is the sum of the decimal places found in Step 2;
Position the decimal point into the product calculated in Step 1.
Let us demonstrate this technique with the following worked examples.
Multiply 3.6 by 2.3
Ignoring the decimal places, we obtain 36 × 23 = 826.
Both decimals, 3.6 and 2.3 have one decimal place each.
The sum of these decimal places is two.
Thus, the product of 36 × 23 = 826 must have two decimal places.
Putting in the decimal point, we obtain 3.6 × 2.3 = 8.26.
Multiplication of Decimals with Whole Numbers
Multiply 5.7 by 8
Ignoring the decimal places, we obtain 57 × 8 = 456.
The decimal 5.7 has one decimal place while the whole number 8 has no decimal place.
The sum of these decimal places is one.
Thus, the product of 57 × 8 = 456 must have one decimal place.
Putting in the decimal point, we obtain 5.7 × 8 = 45.6.
Multiplication of Two Unlike Decimals
Multiply 2.165 by 9.1
Ignoring the decimal places, we obtain 2165 × 91 = 197015.
The decimals 2.165 and 9.1 have 3 decimal places and one decimal place respectively.
The sum of these decimal places is four.
Thus, the product of 2165 × 91 = 197015 must have four decimal places.
Putting in the decimal point, we obtain 2.165 × 9.1 = 19.7015.
Multiplication of Decimals by Powers of 10
When multiplying decimals by powers of 10, we simply move the decimal point to the right based on the number of zeros present in the power of 10. Below are two worked examples.
Multiply 3.87 by 100
There are two zeros in the number 100, so we must shift the decimal point of 3.87 to two places to the right.
3.87 × 100 = 387
Multiply 7.3956 by 1000
There are three zeros in the number 1000, so we must shift the decimal point of 7.3956 three places to the right.
7.3956 × 1000 = 7395.6
Dividing Decimals
When dividing numbers in general, it is always easier to divide by a whole number.
The divisor is the number we divide by. For example, in the expression 32 ÷ 2.3, 32 is the dividend and 2.3 is the divisor.
Below are the essential steps for dividing decimals.
Convert the divisor into a whole number by multiplying it by a power of 10;
Multiply the dividend by the same power of 10 found in Step 1;
Divide these numbers using long division.
The following worked examples show the application of this approach.
The answer in Step 3 gives us the same yield as if e had divided the decimals.
Divide 4.62 by 0.12
Here, we have 4.62 ÷ 0.12 where the dividend is 4.62 and the divisor is 0.12.
To change the divisor into a whole number, we multiply it by 100. This yields 0.12 × 100 = 12.
Multiplying this same value to the dividend, we obtain 4.62 × 100 = 462.
Thus, we have 462 ÷ 12 which is the same as 4.62 ÷ 0.12.
Conducting long division, we obtain
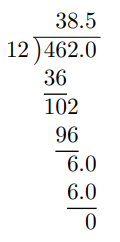
Thus, 4.62 ÷ 0.12 = 38.5.
Division of Decimals with Whole Numbers
Divide 5.525 by 5
Here, we have 5.525 ÷ 5 where the dividend is 5.525 and the divisor is 5.
The divisor is already in the form of a whole number. However, the dividend is still in the form of a decimal.
To tackle this problem, we shall conduct long division while ignoring the decimal point of the dividend.
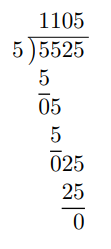
We shall now place the decimal point of the answer directly above the decimal point of the dividend as below.
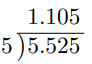
Thus, 5.525 ÷ 5 = 1.105.
Division of Two Unlike Decimals
Divide 3.432 by 1.04
Here, we have 3.432 ÷ 1.04 where the dividend is 3.432 and the divisor is 1.04.
To change the divisor into a whole number, we multiply it by 100. This yields 1.04 × 100 = 104.
Multiplying this same value to the dividend, we obtain 3.432 × 100 = 343.2.
Thus, we have 343.2 ÷ 104 which is the same as 3.432 ÷ 1.04.
Although the divisor is already in the form of a whole number, the dividend is still in the form of a decimal.
As before, we shall conduct long division while ignoring the decimal point of the dividend.
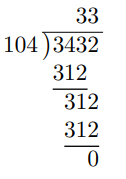
We shall now place the decimal point of the answer directly above the decimal point of the dividend as below.
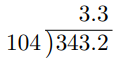
Thus, 3.432 ÷ 1.04 = 3.3.
Division of Decimals by Powers of 10
When dividing decimals by powers of 10, we simply move the decimal point to the left based on the number of zeros present in the power of 10. Below are two worked examples.
Divide 2.34 by 10
There is one zero in the number 10, so we must shift the decimal point of 2.34 one place to the left.
2.34 ÷ 10 = 0.234.
Divide 17635.6 by 1000
There are three zeros in the number 1000, so we must shift the decimal point of 17635.6 three places to the left.
17635.6 ÷ 1000 = 17.6356
Mixed Operations with Decimals
In this section, we shall make use of the PEMDAS order of operations for decimals. Below are some worked examples.
Evaluate.
Solution
We begin by converting the percentage term
4.5% = 4.5 ÷ 100 = 0.045
We can now perform subtraction as usual
Thus, the final answer is 0.078
Evaluate .
Solution
We begin by converting the fraction term
We can now perform addition as usual
Thus, the final answer is 1.32
Evaluate.
Solution
We shall first calculate the expression inside the parenthesis
Next, we shall conduct multiplication
Finally, we shall perform subtraction
Thus, the final answer is 7.9004.
Evaluate.
Solution
We shall first calculate the expression in the grouping
For an expression in the form of a grouping, always remember to solve the numerator before the denominator
Next, we shall conduct addition
Finally, we shall perform subtraction
Thus, the final answer is 3.8.
Evaluate .
Solution
We shall first calculate the expression inside the parenthesis
Next, we shall derive the exponent
Following this, we shall conduct division
Finally, we shall conduct addition
Thus, the final answer is 0.9025.
Operations with Decimals - Key takeaways
- The order of operations for decimals obeys PEMDAS: Parenthesis, Exponent, Multiplication/Division, Addition/Subtraction
- Steps for adding and subtracting decimals
Write down the numbers in column form. Make sure the decimal points are lined up
Put in zeros so that the numbers are of the same length
Add or subtract using column addition or column subtraction
- Steps for multiplying decimals
Remove the decimal points and multiply the numbers
Count the number of decimal places in each given number. Find its sum
The place value of the final answer is the sum of the decimal places derived in Step 2
- Steps for dividing decimals
Convert the divisor into a whole number by multiplying it by a power of 10
Multiply the dividend by the same power of 10 found in Step 1
Divide these numbers using long division
When multiplying decimals by powers of 10, we simply shift the decimal point to the right according to the number of zeros in the power of 10.
When dividing decimals by powers of 10, we simply shift the decimal point to the left according to the number of zeros in the power of 10.